The annual migration of birds is one of nature's most spectacular phenomena, with billions of birds traversing continents in search of favorable climates and abundant food. In recent years, the field of eco-informatics has revolutionized our understanding of these migratory patterns by leveraging satellite cloud imagery to track and analyze the routes taken by these avian travelers. This innovative approach combines ecological science with advanced data analytics, providing unprecedented insights into the behavior and challenges faced by migratory species.
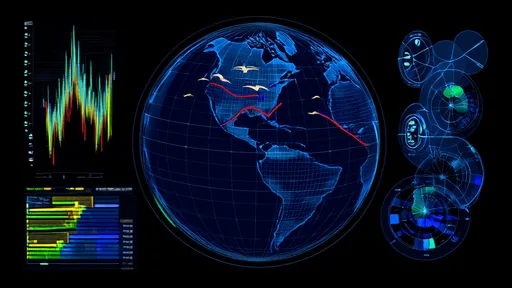
Satellite cloud imagery, traditionally used for weather forecasting, has found a new application in the study of bird migration. By analyzing cloud patterns and atmospheric conditions, researchers can infer the presence of large flocks of birds moving across vast distances. The density and movement of clouds often correlate with the flight paths of migratory birds, as these creatures tend to follow favorable wind currents and avoid adverse weather. This indirect method of tracking allows scientists to monitor migrations on a global scale without the need for physical tagging, which can be invasive and logistically challenging.
The integration of satellite data with ecological models has opened new avenues for understanding the timing and routes of bird migrations. For instance, researchers have discovered that certain species rely on specific atmospheric conditions to optimize their energy expenditure during long flights. By cross-referencing historical migration data with satellite imagery, scientists can predict future migratory patterns with remarkable accuracy. This predictive capability is crucial for conservation efforts, as it enables policymakers to anticipate and mitigate potential threats along migratory corridors.
One of the most striking findings from this research is the identification of key stopover sites—locations where birds rest and refuel during their journeys. These sites are often critical to the survival of migratory species, yet they are increasingly threatened by human activities such as urbanization and agriculture. Satellite cloud analysis has highlighted the importance of preserving these habitats, as disruptions to stopover sites can have cascading effects on entire populations. Conservationists are now using this data to advocate for the protection of these vital areas, ensuring that migratory birds have safe passage across continents.
Climate change adds another layer of complexity to the study of bird migration. Shifts in temperature and weather patterns are altering the availability of food and suitable habitats, forcing birds to adapt their traditional routes. Satellite imagery has revealed that some species are migrating earlier in the year or taking longer, more circuitous paths to reach their destinations. These changes underscore the need for continuous monitoring and adaptive conservation strategies. By tracking these shifts in real-time, researchers can provide early warnings about the impacts of climate change on avian populations.
The use of satellite cloud imagery in eco-informatics is not without its challenges. Interpreting cloud data requires sophisticated algorithms and a deep understanding of both meteorology and ornithology. False positives—such as mistaking dense cloud formations for bird flocks—can skew results, necessitating careful validation through ground observations and other tracking methods. Despite these hurdles, the potential of this technology to transform our understanding of bird migration is immense. As satellite resolution and data processing capabilities improve, so too will the precision and reliability of these analyses.
Beyond scientific research, the insights gained from satellite-based migration studies have practical applications for aviation safety and public health. Bird strikes pose a significant risk to aircraft, particularly during peak migration seasons. By sharing migration data with aviation authorities, researchers can help reduce the likelihood of collisions. Similarly, understanding the movement patterns of birds is essential for monitoring the spread of avian-borne diseases, which can have implications for both wildlife and human populations. The interdisciplinary nature of this work highlights its far-reaching significance.
Looking ahead, the field of eco-informatics promises to unlock even deeper insights into the mysteries of bird migration. Emerging technologies, such as machine learning and high-resolution satellite sensors, are poised to enhance our ability to track and interpret migratory behaviors. Collaborative efforts between scientists, governments, and conservation organizations will be key to harnessing this potential. As we continue to refine our methods, the stories written in the clouds by migrating birds will become ever clearer, guiding efforts to protect these remarkable travelers for generations to come.
In the grand tapestry of life on Earth, the migration of birds is a thread that connects ecosystems across the globe. Through the lens of satellite cloud imagery and eco-informatics, we are beginning to appreciate the intricate patterns and delicate balances that sustain these journeys. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding of the natural world but also empowers us to act as stewards of its preservation. The skies, it seems, have much to teach us—if only we know how to look.

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025
By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025
By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025
By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025

By /Jul 18, 2025
By /Jul 18, 2025